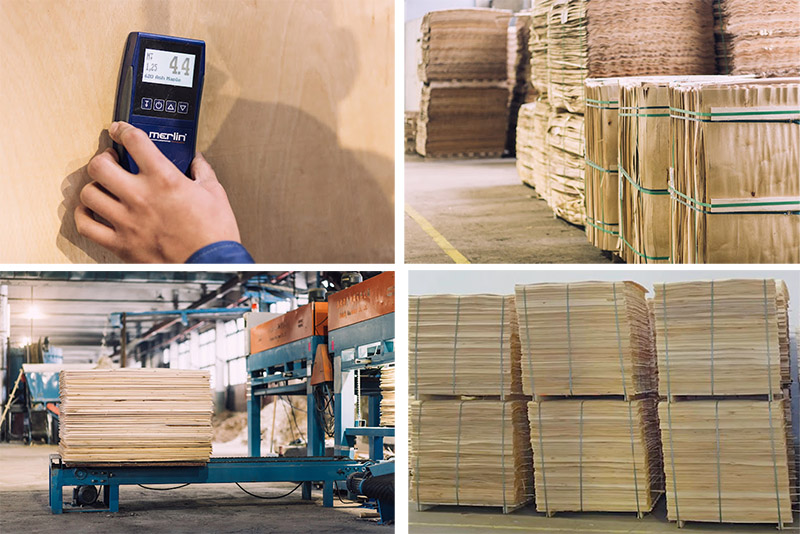
Technical veneer and technical veneer production process
The concept of technological veneer
Technological veneer is scientifically known as reconstructed decorative veneer, which is a kind of artificial wood veneer used for imitation of natural wood grain. Technological veneer is a wood surface material processed by modern scientific and technological means. It retains the texture and feel of natural wood through advanced production technology, while enhancing the physical properties of wood, such as wear resistance and corrosion resistance. The emergence of technological veneer provides more abundant and high-quality material options for furniture, construction and other fields.
The production process of Technical veneer mainly includes the following steps:
Material selection and softening treatment: First, select logs with uniform texture, straight texture and easy cutting. In order to improve the subsequent cutting effect, the wood will be softened before peeling. The common method is to soak the wood in hot water to reduce the hardness of the wood, reduce cutting resistance and improve the quality of the veneer.
Peeled veneer: The wood after softening treatment enters the peeling process. The wood is cut into thin slices by the peeling machine, that is, the veneer. The peeling process can obtain high-quality and uniform thickness veneer, which is suitable for subsequent steps such as dyeing and gluing.
Dyeing treatment: The peeled veneer is usually bleached to remove the natural pigments and impurities of the wood to ensure that the color of the veneer is more uniform. Then, according to the requirements of the product, dyeing treatment is carried out to simulate the texture and color of high-end wood and enhance the decorative effect and simulation of the veneer.
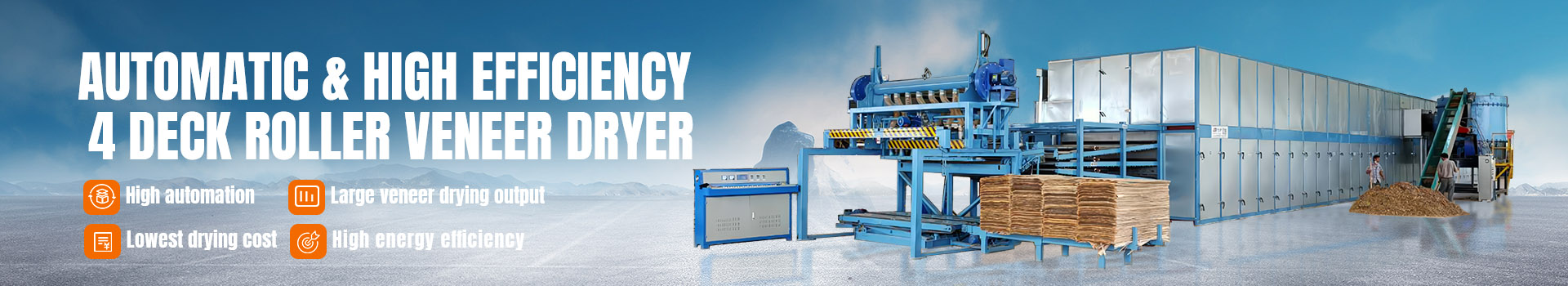
Drying treatment: The dyed veneer is cleaned and the moisture content of the veneer is reduced by drying process. During the drying process, the moisture content of the veneer is usually kept at around 8% to 12%, which can prevent the veneer from warping or deforming during subsequent processing and ensure the stability and quality of the veneer.
Gluing: Layer veneers of different tones and apply glue evenly. The glue used usually has high water resistance and moderate flexibility, so that the veneer is not easy to break and maintains good adhesion during the subsequent planing process.
Lamination: The glued veneers are stacked and combined, and compressed and glued under certain temperature and pressure conditions to completely solidify the glue layer between the veneers and discharge excess moisture. The control of gluing time and pressure is very critical, which will affect the overall stability and strength of the veneer.
Laminating or veneer: To further improve the aesthetics and durability, the surface is sometimes covered with a film or affixed with different types of decorative films. Common films include PVC film, wood grain film, etc., which can give the veneer different textures and colors. It can also protect the veneer surface and avoid cracks or damage after planing.
Slicing: Finally, the formed wood will be planed, and the thickness of the planed veneer is usually between 0.2mm and 2.0mm. Through multiple combinations and planing processes, rich veneer texture effects can be obtained, and more complex patterns and color changes can be achieved.
Trimming and grinding: The edges of the cut wood veneers are trimmed and burrs are removed to ensure the accuracy and appearance quality of the board.
After the above series of processing, the technical veneer can not only simulate the texture and color of high-end wood in appearance, but also effectively guarantee its stability and durability. This makes the technical veneer widely used in furniture, interior decoration, flooring and other fields, becoming an ideal decorative material in modern home and building decoration. By continuously optimizing the production process and improving quality control, the technical veneer is gradually replacing natural wood, showing great advantages in environmental protection and cost control.